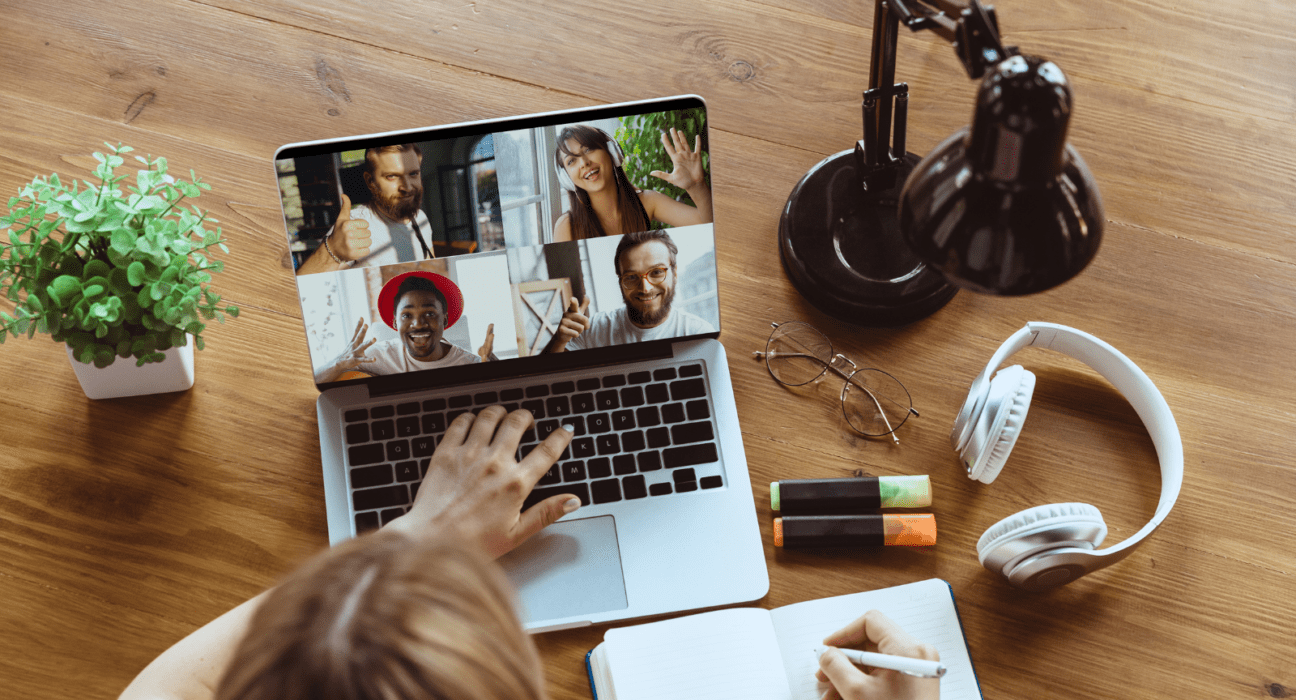
In a world where office buildings once symbolized productivity and corporate success, the concept of remote work has surged from a niche trend into a global phenomenon. The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst, accelerating a shift that was already underway. As we step into an era where remote work is no longer an exception but a norm, it’s essential to examine how this shift is transforming the landscape of work, its advantages and challenges, and what the future might hold.
The Evolution of Remote Work
Remote work has evolved from a temporary solution to a long-term strategy. Before the pandemic, remote work was often limited to a handful of industries and roles. It was seen as a perk for employees or a necessity for freelancers and digital nomads. Fast forward to today, and many companies have adopted flexible work policies as a core part of their business model.
Innovations in technology have played a crucial role in this transformation. Tools like Zoom, Slack, and Asana have made it possible to communicate, collaborate, and manage projects from anywhere in the world. With the click of a button, teams can now bridge geographical divides, creating a more interconnected and dynamic work environment.
The Pros of Remote Work
1. Flexibility and Work-Life Balance
One of the most celebrated benefits of remote work is the flexibility it offers. Employees can design their work schedules around personal commitments, leading to a better work-life balance. This flexibility not only improves employee satisfaction but can also enhance productivity. According to a study by Stanford University, remote workers are 13% more productive than their in-office counterparts.
2. Cost Savings
Remote work can also lead to significant cost savings for both employees and employers. Employees save on commuting expenses, work attire, and daily meals. Employers, on the other hand, can reduce overhead costs associated with office space, utilities, and equipment. For companies with a global workforce, remote work also means access to a broader talent pool without the constraints of geographic location.
3. Environmental Impact
With fewer people commuting to work, there’s a noticeable reduction in carbon emissions. Remote work contributes to a decrease in traffic congestion and pollution, making it a more environmentally friendly option. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability and corporate social responsibility.
The Cons of Remote Work
1. Communication Challenges
Despite the technological advancements, remote work can pose significant communication challenges. Without face-to-face interactions, misunderstandings and miscommunications are more likely. The lack of physical presence can also lead to feelings of isolation and disconnection from the team, impacting collaboration and morale.
2. Distractions and Home Environment
Working from home can blur the lines between personal and professional life, making it difficult to stay focused. Distractions such as household chores, family members, or pets can interrupt workflow. Additionally, not everyone has a dedicated workspace, which can affect productivity and comfort.
3. Career Advancement and Networking
Remote work can sometimes limit opportunities for career advancement and networking. Employees may find it harder to make meaningful connections or gain visibility in their organization. This can impact their professional growth and opportunities for promotions.
The Future of Remote Work
As we look to the future, several trends are shaping the evolution of remote work:
1. Hybrid Work Models
Many organizations are adopting hybrid work models, combining remote work with in-office presence. This approach aims to offer the best of both worlds—flexibility for employees and the opportunity for in-person collaboration. Hybrid models also address some of the communication and networking challenges associated with fully remote work.
2. Advances in Technology
Technology will continue to drive the evolution of remote work. Innovations in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) could create more immersive work environments, enhancing remote collaboration and team dynamics. AI-driven tools will also play a role in automating routine tasks and improving productivity.
3. Focus on Employee Well-Being
The future of remote work will likely place a stronger emphasis on employee well-being. Companies are expected to invest in mental health resources, virtual team-building activities, and strategies to combat isolation. The shift towards a more human-centric approach will be crucial in maintaining a motivated and engaged workforce.
4. Global Talent Pools
Remote work breaks down geographical barriers, enabling companies to tap into a diverse global talent pool. This trend is expected to continue, with organizations seeking talent from different regions and cultures to drive innovation and growth.
Final Thought
The rise of remote work marks a significant shift in how we approach employment and productivity. While it offers numerous benefits, such as flexibility, cost savings, and environmental impact, it also presents challenges that need to be addressed. As technology advances and work practices evolve, the future of remote work holds exciting possibilities. Embracing a balanced approach that leverages the strengths of remote work while addressing its challenges will be key to thriving in this new era of work.
Additional resources: